Introduction
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is a common yet often misunderstood mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life, including work, health, relationships, and daily responsibilities. Unlike normal anxiety, which arises in response to specific stressors, GAD is chronic and can interfere with daily functioning. In this article, we will explore what GAD is, its symptoms, causes, risk factors, and possible treatment options.
Understanding Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
GAD is classified as an anxiety disorder that involves excessive, uncontrollable worry for at least six months. It can affect individuals of all ages and backgrounds, significantly impacting their personal and professional lives. While everyone experiences anxiety from time to time, people with Generalized Anxiety Disorder GAD find it difficult to control their worries, leading to emotional and physical distress.
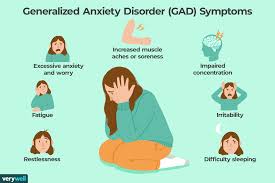
Symptoms of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
GAD symptoms can vary from person to person, but they typically fall into two main categories: emotional and physical symptoms.
Emotional Symptoms
- Excessive Worrying – A persistent and overwhelming sense of worry that is difficult to control.
- Restlessness – Feeling on edge, unable to relax, or constantly nervous.
- Irritability – Becoming easily annoyed or frustrated over small issues.
- Difficulty Concentrating – Trouble focusing on tasks, often feeling mentally drained.
- Feeling Overwhelmed – A sense of impending doom or feeling as though something bad will happen.
Physical Symptoms
- Fatigue – Feeling constantly tired despite getting enough rest.
- Muscle Tension – Experiencing tightness or soreness in the muscles, particularly in the neck and shoulders.
- Headaches – Frequent tension headaches caused by prolonged stress.
- Digestive Issues – Stomach pain, nausea, diarrhea, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Sleep Disturbances – Difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restless sleep.
Causes of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
The exact cause of GAD is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development. These include:
Biological Factors
- Genetics – A family history of anxiety disorders increases the likelihood of developing GAD.
- Brain Chemistry – Imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, can affect mood regulation.
- Hormonal Changes – Fluctuations in hormones, especially during stressful periods, can trigger anxiety.
Environmental Factors
- Chronic Stress – Prolonged exposure to stressful situations can lead to heightened anxiety.
- Trauma – Experiencing traumatic events, such as abuse or accidents, can contribute to GAD.
- Substance Abuse – Excessive use of alcohol, drugs, or caffeine can worsen anxiety symptoms.
Risk Factors for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Several risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing GAD, including:
- Family History – If close relatives have an anxiety disorder, the risk is higher.
- Personality Traits – Perfectionists and highly self-critical individuals may be more prone to GAD.
- Chronic Illness – Conditions such as heart disease or diabetes can increase stress and anxiety levels.
- Major Life Changes – Events like job loss, divorce, or relocation can contribute to anxiety.
- Childhood Adversity – Growing up in a stressful or abusive environment can increase vulnerability.
Diagnosing Generalized Anxiety Disorder
A proper diagnosis of GAD requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. The process typically includes:
- Clinical Interview – Discuss symptoms, medical history, and family history of anxiety disorders.
- Psychological Questionnaires – Assessing the severity and frequency of anxiety symptoms.
- Physical Examination – Ruling out medical conditions that may mimic anxiety symptoms.
- Diagnostic Criteria – Meeting the guidelines outlined in the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders).
Treatment Options for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
GAD is a manageable condition with the right treatment approach. The most common treatments include:
Psychotherapy
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) – Helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns.
- Mindfulness-Based Therapy – Focuses on staying present and managing anxious thoughts.
- Exposure Therapy – Gradual exposure to anxiety-provoking situations to reduce fear response.
Medications
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) – Such as fluoxetine and sertraline, help regulate mood.
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) – Such as venlafaxine, effective for anxiety relief.
- Benzodiazepines – Short-term use for severe anxiety, though they can be addictive.
- Beta-Blockers – Help reduce physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat and trembling.
Lifestyle Changes
- Regular Exercise – Physical activity releases endorphins, improving mood and reducing anxiety.
- Healthy Diet – Avoid caffeine and processed foods while consuming nutritious meals.
- Adequate Sleep – Establishing a bedtime routine and limiting screen time before bed.
- Relaxation Techniques – Practicing yoga, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation.
Coping Strategies for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
In addition to professional treatment, self-help strategies can improve quality of life:
- Journaling – Writing down thoughts and emotions to reduce stress.
- Social Support – Talking to friends, family, or support groups for encouragement.
- Time Management – Organizing daily tasks to reduce feelings of overwhelm.
- Setting Realistic Goals – Breaking large tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
- Limiting News Consumption – Reducing exposure to negative media that may trigger anxiety.
When to Seek Professional Help
It is important to seek help if anxiety symptoms:
- Interfere with daily life and responsibilities.
- Cause significant distress or emotional suffering.
- Lead to avoidance of social interactions and work obligations.
- Resulting in physical symptoms that persist despite lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Generalized Anxiety Disorder is a serious but treatable condition that affects many individuals worldwide. Recognizing the symptoms early, seeking professional help, and implementing effective treatment strategies can significantly improve well-being. If you or someone you know is struggling with excessive worry and anxiety, consulting a mental health professional can provide relief and support. With the right approach, it is possible to manage GAD and lead a fulfilling life.